Novel Test from Quest Diagnostics Helps Diagnose and Monitor Rheumatoid Arthritis
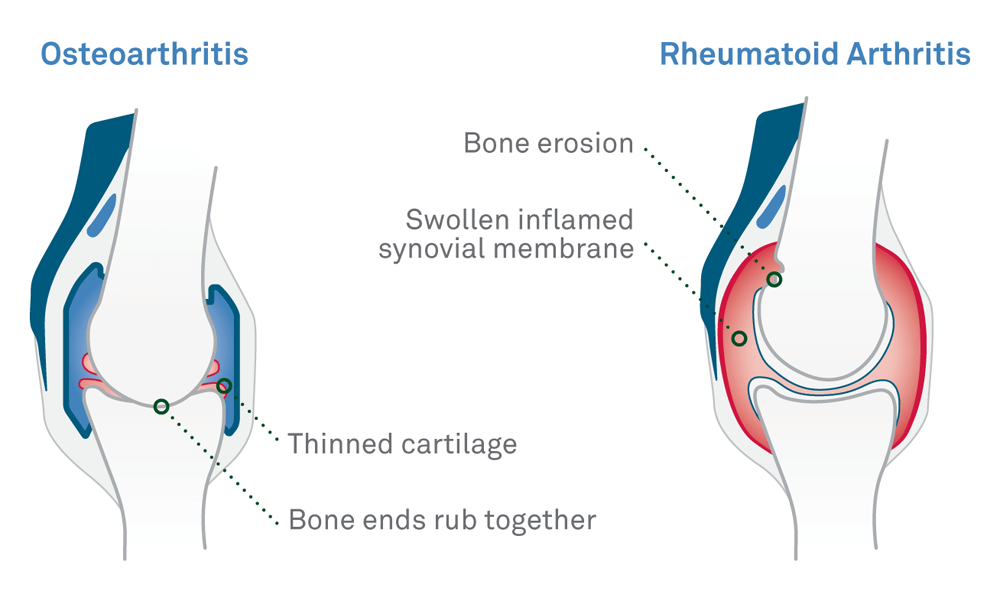
There are more than 100 forms of arthritis. One of the most prevalent and potentially disabling is rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Differential diagnosis, as well as early diagnosis of RA is difficult, as patients may present with nonspecific symptoms involving joint pain and stiffness.Early diagnosis of RA is critical because treatment of patients with RA with newer therapies is beneficial, especially when initiated in early stages of disease. However, standard tests like erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), including rheumatoid factor (RF) and cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) tests are positive very late in the disease state or positive in only about 50 percent cases accurate thus making the diagnosis of RA difficult.
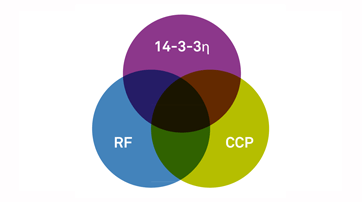
Combining testing for 14-3-3eta protein (the only biomarker produced exclusively in the joint) with rheumatoid factor (RF) and cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) tests enhances the detection of rheumatoid arthritis.To help improve the early diagnosis of RA , Quest Diagnostics became the first diagnostic service provider to launch testing based on the 14-3-3eta protein biomarker, in 2013. Combining testing for this novel biomarker with RF and CCP tests enhances the detection of RA up to 78 percent. Today, physicians across the United States can order all three tests together as the Quest Diagnostics IdentRA® panel or any one of the test separately.In addition to early diagnosis, patients benefit from consistent and objective monitoring of disease progression. Monitoring RA is important because the disease is chronic and fluctuates. Monitoring is mostly performed clinically by the physician (rheumatologists) based on physical evaluation and symptoms shared by the patient. However, clinical assessment of symptoms has its limitations. Besides providing insight for early diagnosis. more recent studies demonstrate that 14-3-3eta can be beneficial in assessing disease severity and for monitoring disease progression.
Additionally, 14-3-3eta testing can help clinicians identify and predict remission with tocilizumab, a common biological therapy. The study in Arthritis Research and Therapy demonstrates that baseline 14-3-3eta measurement is an independent predictor of remission (as defined by DAS28-ESR) in patients treated with tocilizumab and a decrease in 14-3-3eta in response to tocilizumab therapy is associated with better outcomes, while an increase implies worse prognosis. This may have implications for monitoring progression with other therapies.The Arthritis Research & Therapy studies cited above provide evidence on the clinical utility of 14-3-3eta as an important test in aiding diagnosis of RA early and helping clinicians monitor the disease progression and also to choose a treatment regimen that will produce the best outcomes for that patient. Maksymowych WP, Naides SJ, Bykerk V, et al. Serum 14-3-3η is a novel marker that complements current serological measurements to enhance detection of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2014;41;2104–2113. Carrier N, Marotta A, de Brum-Fernandes AJ, et al. Serum levels of 14-3-3η protein supplement C-reactive protein and rheumatoid arthritis-associated antibodies to predict clinical and radiographic outcomes in a prospective cohort of patients with recent-onset inflammatory polyarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18:37. Hirata S, Marotta A, Gui Y, et al. Serum 14-3-3η level is associated with severity and clinical outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis, and its pretreatment level is predictive of DAS28 remission with tocilizumab. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:280.
Improving Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosis

Combining testing for 14-3-3eta protein (the only biomarker produced exclusively in the joint) with rheumatoid factor (RF) and cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) tests enhances the detection of rheumatoid arthritis.To help improve the early diagnosis of RA , Quest Diagnostics became the first diagnostic service provider to launch testing based on the 14-3-3eta protein biomarker, in 2013. Combining testing for this novel biomarker with RF and CCP tests enhances the detection of RA up to 78 percent. Today, physicians across the United States can order all three tests together as the Quest Diagnostics IdentRA® panel or any one of the test separately.In addition to early diagnosis, patients benefit from consistent and objective monitoring of disease progression. Monitoring RA is important because the disease is chronic and fluctuates. Monitoring is mostly performed clinically by the physician (rheumatologists) based on physical evaluation and symptoms shared by the patient. However, clinical assessment of symptoms has its limitations. Besides providing insight for early diagnosis. more recent studies demonstrate that 14-3-3eta can be beneficial in assessing disease severity and for monitoring disease progression.
How Detecting 14-3-3eta Helps
Detecting 14-3-3eta in patients can help primary care physicians prioritize patients for rapid referral to rheumatologists and facilitate early intervention with biological therapies. In a study published in Arthritis Research &Therapy, researchers found that serum levels of 14-3-3eta protein supplement C-reactive protein (CRP) to predict clinical and radiographic outcomes in a prospective cohort of patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. The 14-3-3eta protein >= 0.50 ng/mL and CRP >= >8.0 mg/L predict poor clinical and radiographic outcomes, a high risk of clinically refractory RA disease, and significant joint damage over the next five years. These findings suggest that high serum levels of 14-3-3eta and CRP at baseline and during treatment both independently and together represent poor prognosis.
Additionally, 14-3-3eta testing can help clinicians identify and predict remission with tocilizumab, a common biological therapy. The study in Arthritis Research and Therapy demonstrates that baseline 14-3-3eta measurement is an independent predictor of remission (as defined by DAS28-ESR) in patients treated with tocilizumab and a decrease in 14-3-3eta in response to tocilizumab therapy is associated with better outcomes, while an increase implies worse prognosis. This may have implications for monitoring progression with other therapies.The Arthritis Research & Therapy studies cited above provide evidence on the clinical utility of 14-3-3eta as an important test in aiding diagnosis of RA early and helping clinicians monitor the disease progression and also to choose a treatment regimen that will produce the best outcomes for that patient. Maksymowych WP, Naides SJ, Bykerk V, et al. Serum 14-3-3η is a novel marker that complements current serological measurements to enhance detection of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2014;41;2104–2113. Carrier N, Marotta A, de Brum-Fernandes AJ, et al. Serum levels of 14-3-3η protein supplement C-reactive protein and rheumatoid arthritis-associated antibodies to predict clinical and radiographic outcomes in a prospective cohort of patients with recent-onset inflammatory polyarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18:37. Hirata S, Marotta A, Gui Y, et al. Serum 14-3-3η level is associated with severity and clinical outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis, and its pretreatment level is predictive of DAS28 remission with tocilizumab. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:280.
Buy your own lab tests
Shop online for a Rheumatoid Arthritis Test - no doctor visit required for purchase





